Ultimate Guide to Building a Powerful IT Security Strategy in Kenya (2025 Edition)
Introduction to IT Security in Kenya
In today’s digital era, the backbone of any successful business or organization is a well-structured IT security strategy. In Kenya, as more companies adopt digital solutions, the need for robust cybersecurity has grown exponentially. Kenya’s vision to become a regional tech hub makes this need even more critical.
The country boasts a rapidly growing ICT sector, with innovations in mobile money, e-commerce, and smart government services. However, these advancements also attract cybercriminals. A solid IT security framework isn’t just advisable—it’s essential.
The Rising Cyber Threat Landscape in Kenya
Kenyan organizations face various cyber threats, ranging from data breaches and ransomware attacks to phishing scams. Some of the most prevalent threats include:
- Phishing emails targeting banks and telecom companies
- Malware attacks against SMEs and educational institutions
- Ransomware disabling healthcare and financial systems
A notable example is the 2022 attack on the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA), which exposed sensitive taxpayer data and forced system downtimes.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
Kenya has made significant strides in establishing a regulatory environment for IT security. Key components include:
- Data Protection Act, 2019: Enforces data privacy, regulates data processors, and outlines breach notification rules.
- Communications Authority of Kenya (CAK): Oversees cybersecurity policy and national infrastructure protection.
- ISO/IEC 27001 Certification: Encouraged for businesses seeking global cybersecurity compliance.
Organizations are now expected to comply with these regulations or face legal and financial penalties.
Building Blocks of an Effective IT Security Strategy
To build a strong IT security strategy in Kenya, companies should start with:
Risk Assessment and Vulnerability Analysis
- Identify critical assets
- Evaluate potential threats
- Map vulnerabilities across hardware, software, and human elements
Policy Development and Enforcement
- Draft and implement cybersecurity policies
- Define roles and responsibilities
- Establish access control and authentication protocols
These building blocks form the foundation of a proactive and resilient cybersecurity posture.
Governance and Leadership in Cybersecurity
Top-level leadership plays a pivotal role in cybersecurity. Kenyan firms are increasingly adopting structured governance models that include:
- Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) to oversee strategic planning
- Cybersecurity committees to ensure policies align with organizational goals
- Board-level oversight of cyber risks and incident response readiness
Infrastructure Security Measures
To protect their core IT infrastructure, Kenyan organizations must invest in:
- Firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS)
- Antivirus software and patch management protocols
- Virtual private networks (VPNs) for remote employees
Proper infrastructure security helps reduce attack surfaces and contain potential breaches.
Cloud and Data Security Considerations
Cloud adoption is rising in Kenya, especially among fintech and government institutions. Best practices include:
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Role-based access controls (RBAC)
Using secure cloud platforms that comply with local laws is vital for protecting sensitive data.
Employee Awareness and Training Programs
Employees are the weakest link—or strongest defense—depending on their training. Kenyan companies should:
- Conduct cyber hygiene workshops
- Simulate phishing attack drills
- Include cybersecurity in employee onboarding
Regular training improves threat detection and response capabilities across the board.
Incident Response Planning and Management
Preparedness is key. A robust incident response (IR) strategy includes:
- A documented incident response plan (IRP)
- Defined communication protocols
- A trained Cybersecurity Incident Response Team (CSIRT)
This enables swift and coordinated action when breaches occur.
Cybersecurity Tools and Technologies
Technology helps enforce policy and detect anomalies. Recommended tools for Kenya-based firms include:
- SIEM systems like Splunk or IBM QRadar
- Antivirus software such as Bitdefender or Kaspersky
- Threat intelligence platforms (TIPs)
AI-powered tools are increasingly used for proactive detection and real-time response.
Vendor and Third-Party Risk Management
Third-party vendors often pose security risks. Best practices in Kenya include:
- Performing vendor risk assessments
- Requiring security certifications
- Including cyber clauses in contracts
This helps secure supply chains and minimize indirect threats.
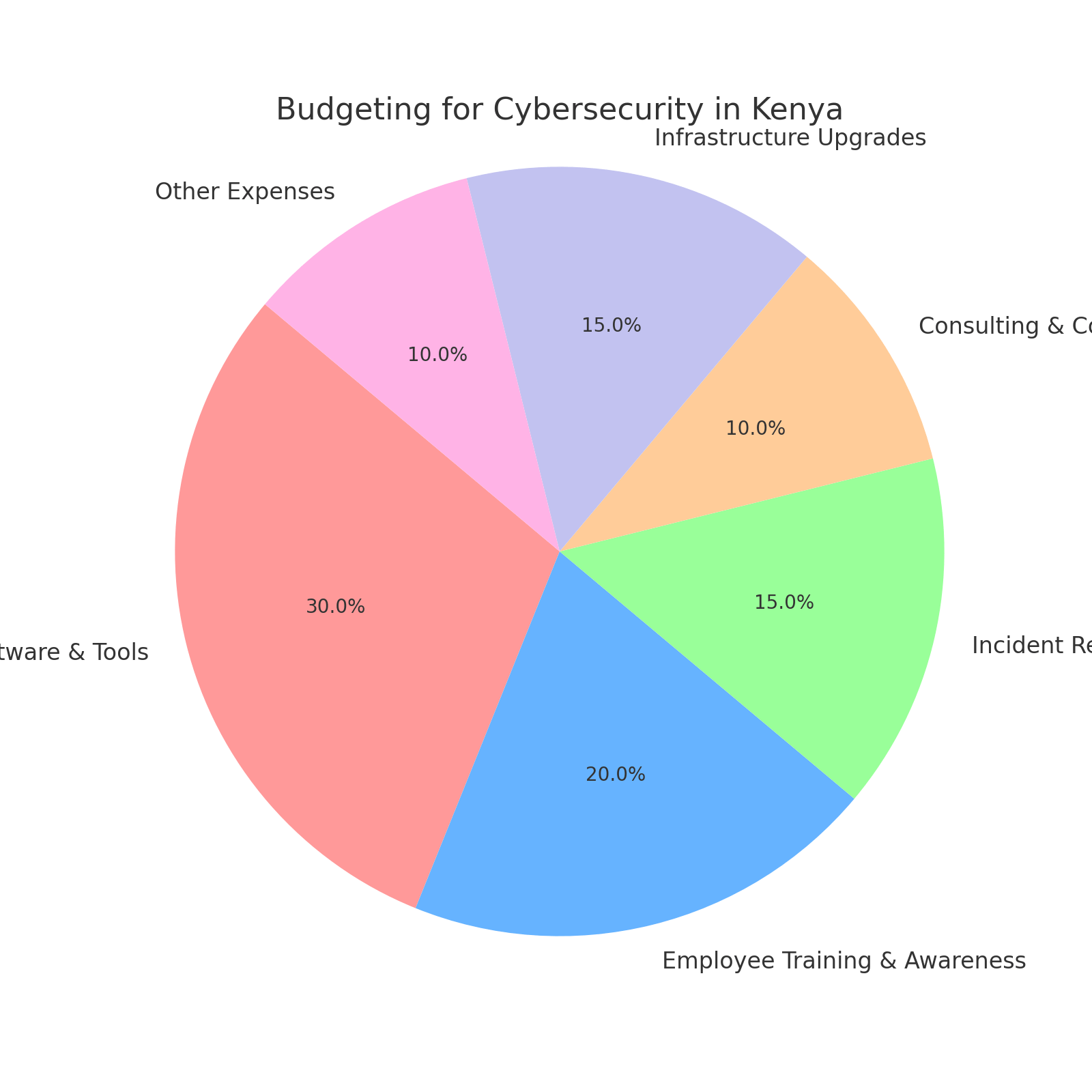
Budgeting for Cybersecurity in Kenya
Many businesses in Kenya struggle with budgeting for IT security. However, an effective plan requires:
- Clear cost estimates for software, training, and consulting
- ROI analysis to justify security investments
- Seeking funding from government grants or NGOs
Cybersecurity should be treated as a business enabler, not an expense.
Public-Private Partnerships in Enhancing Cybersecurity
Several collaborations are helping build Kenya’s cyber resilience:
- Academic partnerships (e.g., Strathmore University’s Centre for IT Policy and Law)
- NGO support from organizations like AfricaCERT
- Government-led initiatives such as the National Cybersecurity Strategy
These partnerships offer training, intelligence sharing, and policy development support.
Trends and Future of IT Security in Kenya
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping Kenya’s cybersecurity landscape:
- Increased AI integration for faster threat detection
- Zero Trust architecture adoption
- Greater emphasis on privacy with the enforcement of data protection laws
As Kenya gears up for 5G, digital transformation will require stronger, scalable IT security frameworks.
Case Studies of Successful IT Security Implementations in Kenya
Safaricom’s Approach
- Implements 24/7 threat monitoring
- Trains staff using simulated cyber-attack exercises
- Partners with global cybersecurity experts
Kenyan Banks
- Use end-to-end encryption
- Regularly undergo penetration testing
- Employ multi-factor authentication for online banking
These examples show that with commitment, successful security strategies are achievable.
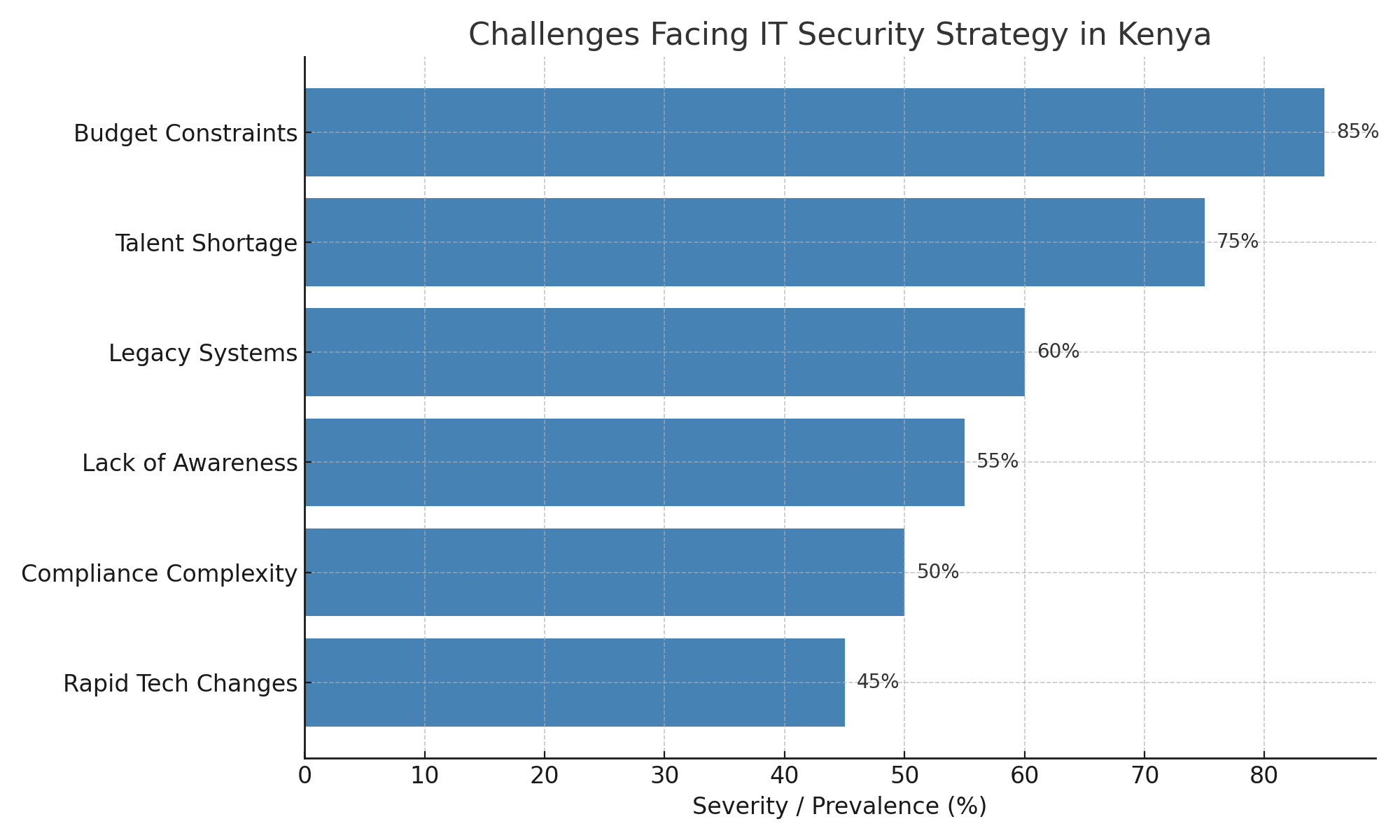
Challenges Facing IT Security Strategy in Kenya
Despite progress, some challenges persist:
- Budget constraints, especially among SMEs
- Shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals
- Legacy systems still in use across sectors
Tackling these issues requires coordinated policy and workforce development efforts.
Best Practices and Recommendations
Here are key takeaways for Kenyan organizations:
- Conduct regular audits of systems and policies
- Keep software updated with patches
- Limit user access based on roles
- Educate staff continuously
- Back up data regularly and securely
Implementing these practices improves security posture and resilience.
FAQs About IT Security Strategy Kenya
Q1: Why is IT security important for businesses in Kenya?
A1: It protects sensitive data, ensures business continuity, and prevents financial and reputational losses due to cyberattacks.
Q2: What laws regulate IT security in Kenya?
A2: The Data Protection Act and the Kenya Information and Communications Act govern cybersecurity practices.
Q3: How can small businesses in Kenya afford cybersecurity?
A3: They can start with basic tools like antivirus and firewalls, seek training grants, or use free resources from government initiatives.
Q4: What is the role of the CAK in IT security?
A4: The CAK enforces policies, monitors threats, and supports national infrastructure protection.
Q5: How often should companies update their IT security strategies?
A5: At least annually, or whenever new threats, technologies, or business changes occur.
Q6: Are there cybersecurity training programs in Kenya?
A6: Yes, offered by universities, the National KE-CIRT/CC, and private training institutes.
Conclusion
Kenya’s digital journey demands a comprehensive, locally adapted IT security strategy. From risk assessments and training to cloud security and vendor management, every aspect plays a vital role. By aligning with regulations, leveraging technology, and investing in human capital, Kenyan businesses can create a resilient cybersecurity foundation that supports sustainable growth.





